|
As has been shown by Boyle's law and Charles' law, the behaviour of gases conforms (to a close approximation) to some simple relationships between the gas volume, pressure and temperature for a given amount of gas. Combining Boyle's law and Charles' law gives the equation of state. Syllabus referenceStructure 1.5.4 - The relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature and amount of an ideal gas is shown in the ideal gas equation PV = nRT and the combined gas law P1V1/T1= P2V2/T2.
Guidance
Tools and links
|
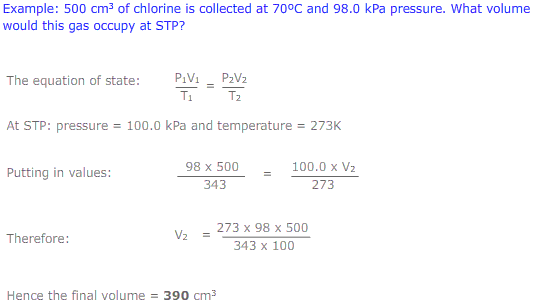
The equation of state
The equations of Boyle's law (PV = constant) and Charles' law (V/T = constant) may be combined to give the expression: PV/T = constant. This is called the equation of state. This new combined gas equation can be used to find the new volume, pressure and temperature of a gas if the conditions are changed.