Standard level
The pH scale provides us with a method of describing the degree of acidity, or basicity of a solution.
Syllabus ref: R3.1.4Reactivity 3.1.4 - The pH scale can be used to describe the [H+] of a solution:
- pH = –log10[H+]; [H+] = 10–pH
- Perform calculations involving the logarithmic relationship between pH and [H+].
Guidance
- Include the estimation of pH using universal indicator, and the precise measurement of pH using a pH meter/probe.
- The equations for pH are given in the data booklet.
Tools and links
- Tool 1, Tool 2, Tool 3 - What is the shape of a sketch graph of pH against [H+]?
- Nature of science, Tool 2 - When are digital sensors (e.g. pH probes) more suitable than analogue methods (e.g. pH paper/solution)?

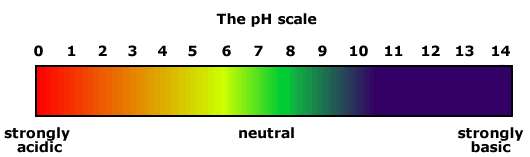
The pH scale
The term 'pH' derives from the french for 'potential hydrogen'. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14.
The pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen. It is defined by the negative of the logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration:
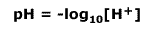
The higher the hydrogen ion concentration the lower the pH value. pH can be measured with a pH meter, or with pH paper (paper containing a mixture of indicators to cause a continuous color change).
| pH | [H+] / mol dm-3 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1 |
|
2
|
0.01
|
|
3
|
1 x 10-3
|
|
4
|
1 x 10-4
|
|
5
|
1 x 10-5
|
|
6
|
1 x 10-6
|
|
7
|
1 x 10-7
|
|
8
|
1 x 10-8
|
|
9
|
1 x 10-9
|
|
10
|
1 x 10-10
|
|
14
|
1 x 10-14
|
As can be seen in the table, a change in pH value of 1 unit is equivalent to a ten-fold change in hydrogen ion concentration.
Example: How many times greater is the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution with pH=1 than a solution with pH=3?
pH1 has a hydrogen ion concentration of 1 x 10-1 mol dm-3. (0.1 mol dm-3)
pH3 has a hydrogen ion concentration of 1 x 10-3 mol dm-3. (0.001 mol dm-3)
Therefore pH1 has a hydrogen ion concentration 100 times greater than pH3.
Strongly acidic
pH 1 represents strong acid, getting progressively weaker as the pH rises. pH 7 is the neutral value of pure water at 25ºC and 1 atmosphere pressure.
If we have two solutions with their pH values, the lower one will be more acidic and the higher one will be more basic (though they could both still be basic/acidic with respect to water at pH 7).
Highly basic
Solutions with a pH of greater than 13 are highly basic. They show blue/purple to universal indicator and blue to litmus.
Highly basic solutions include sodium hydroxide(aq), potassium hydroxide(aq) and barium hydroxide(aq). Such solutions are often said to be 'caustic'. For example 'caustic soda' is an old term for sodium hydroxide. A 0.1 mol dm-3 solution of sodium hydroxide has a pH of 13.
Neutral
Generally considered to be pH 7. This is the pH of pure water at 25ºC. Neutral solutions have no effect on litmus paper and turn Universal indicator green.
Worked examples
QQ831-01 The pH value of a 1.00 x 10-3 mol dm-3 solution of sodium hydroxide is which of the following?- 3
- 8
- 11
- 14
|
The pH = 11 |
QQ831-02 Aqueous solutions of each of the following have a concentration of 0.100 mol dm-3. Which has the highest pH?
- HCl
- CH3COOH
- NaOH
- NH3
|
Highest pH means the most basic (or least acidic) NaOH is a strong base and has the highest pH - response C |
QQ831-03 Solutions P, Q, R and S have the following properties: P: pH = 8, Q: [H+] = 1 x 10-3 mol dm-3, R: pH = 5, S: [H+] = 1 x 10-7 mol dm-3.
When these solutions are arranged in order of increasing acidity (least acidic first) the correct order is:
- P, S, R, Q
- Q, R, S, P
- S, R, P, Q
- R, P, Q, S
|
The highest pH is P (pH = 8) The second highest is S (pH = 7) The third highest is R (pH = 5) The fourth highest is Q (pH = 3) Correct order PSRQ - response A |
QQ831-04 How does the [H+] in an aqueous solution with pH = 4 compare with the [H+] in a solution with a pH = 2? The [H+] is:
- Twice as great
- Half as much
- 1/10 of the value
- 1/100 of the value
|
pH 4 means that the hydrogen ion concentration is 1 x 10-4 mol dm-3. pH 2 means that the hydrogen ion concentration is 1 x 10-2 mol dm-3. 1 x 10-4 is 100 times smaller than 1 x 10-2. Response D |
QQ831-05 When the pH of a solution changes from 2.0 to 4.0, the hydrogen ion concentration:
- increases by a factor of 100.
- increases by a factor of 2.
- decreases by a factor of 2.
- decreases by a factor of 100.
|
pH 2 has a hydrogen ion concentration of 1 x 10-2 mol dm-3 pH 4 has a hydrogen ion concentration of 1 x 10-4 mol dm-3 Therefore a change from pH2 to pH4 decreases the hydrogen ion concentration by a factor of 100 - response D |
QQ831-06 The pH of a solution is 2. If its pH is increased to 6, how many times greater is the [H+] of the original solution?
- 3
- 4
- 1000
- 10000
|
pH 2 has a hydrogen ion concentration of 1 x 10-2 mol dm-3 pH 6 has a hydrogen ion concentration of 1 x 10-6 mol dm-3 Therefore the original solution is 10000 times greater in hydrogen ions - response D |
QQ831-07 When the following 0.10 mol dm-3 solutions are arranged in order of increasing pH (lowest first) what is the correct order?
NH3(aq), NaOH(aq), HCl(aq), CH3COOH(aq)
- NaOH(aq), NH3(aq), CH3COOH(aq), HCl(aq)
- HCl(aq), CH3COOH(aq), NH3(aq), NaOH(aq)
- HCl(aq), CH3COOH(aq), NaOH(aq), NH3(aq)
- NaOH(aq), NH3(aq), HCl(aq), CH3COOH(aq)
|
Lowest pH means the strongest acid, which is HCl(aq) The next strongest acid is CH3COOH(aq) The weakest base is NH3(aq) The strongest base is NaOH(aq) The correct order of increasing pH is HCl(aq), CH3COOH(aq), NH3(aq), NaOH(aq) - response B |
QQ831-08 What will happen if CO2(g) is allowed to escape from the following reaction mixture at equilibrium?
CO2(g) + H2O(l) ⇋ H+(aq) + HCO3-(aq)
- The pH will decrease
- The pH will increase
- The pH will remain constant
- The pH will become zero
|
Using Le Chatelier's principle, removal of a component from the left hand side pulls the equilibrium to the left. Therefore hydrogen ions are removed and the pH of the solution increases (gets less acidic) - response B |
QQ831-09 An acidic solution could have a pH of:
- 7
- 10
- 3
- 14
|
The pH scale runs from 0 acid to 14, base, with the neutral point being pH 7. Response C |
QQ831-10 What is the pH of a 0.00001 molar HCl solution?
- 1
- 9
- 5
- 4
| pH is defined as the negative log10 hydrogen ion concentration.
log(10) of 0.00001 = -5 therefore pH = 5 Response C |