Standard level
Atoms and molecules are pretty small (understatement!) and, as scientists are interested in being able to describe quantities of matter in terms of the mass and number of particles contained per unit mass, this poses a problem.
Measuring the mass of individual atoms, we find that one hydrogen atom has a mass of about 1.66 x 10-27g
This number is far too small to be useful and so it makes sense to deal with quantities of atoms which can be measured in the laboratory.
Syllabus ref: S1.4.1Structure 1.4.1 - The mole (mol) is the SI unit of amount of substance. One mole contains exactly the number of elementary entities given by the Avogadro constant.
- Convert the amount of substance, n, to the number of specified elementary entities.
Guidance
- An elementary entity may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an electron, any other particle or a specified group of particles.
- The Avogadro constant NA is given in the data booklet. It has the units mol–1.
Tools and links

Amedeo Avogadro
The hydrogen standard
Hydrogen is the smallest atom and it was originally used as the standard by which all the other atoms were compared. It was assigned a value of 1 unit and other atoms masses calculated compared to hydrogen atoms.
The 1H isotope has a mass assigned a value of exactly 1 atomic mass unit. This was the original reference.
The 1H isotope
Nowadays the 12C isotope is used as a reference for comparison of relative atomic masses. This isotope has the assigned mass of 12.00000, all other atoms are measured relative to 12C.
The 12C isotope
.gif)
Measured on this scale hydrogen atoms (on average) have a relative mass of 1.00797
Carbon atoms have a relative mass of 12.01111 on average. Although this seems strange at first sight, it is because carbon has several isotopes 12C, 13C, and 14C and the relative mass of carbon is given as the weighted average of all of the isotopes in a naturally occuring sample. Clearly the average must be greater than 12.0000.
Most tables use the relative atomic masses rounded up to one or two decimal places.
Carbon atoms have a mass approximately 12 times that of a hydrogen atom, therefore they have a RELATIVE mass of 12 (there are no units as it is a comparison - see relative measures)
Provided the number of carbon atoms is equal to the number of hydrogen atoms the mass of carbon is always 12 times the mass of hydrogen.
Clearly there will be a specific number of hydrogen atoms that when weighed have a mass of 1g and that the same number of carbon atoms MUST have a mass of 12g. This number, named after its discoverer is called:
Avogadro's constant = 6.02 x 1023
Avogadro's number or constant is the number to which the mass of an atom must be multiplied to give a mass in grams numerically equal to its relative atomic mass.
Example
Hydrogen has a relative atomic mass of 1 therefore 6.02 x 1023 hydrogen atoms have a mass of 1g
Carbon has a relative mass of 12 therefore 6.02 x 1023 carbon atoms have a mass of 12g
Magnesium has a relative atomic mass of 24 therefore 6.02 x 1023 magnesium atoms have a mass of 24g
This gives rise to two important definitions
- The amount of any substance containing an Avogadro number of particles of that substance is called a mole.
- 1 mole of any substance has a mass equal to its relative mass expressed in grams
Example
1 mole of magnesium contains 6.02 x 1023 magnesium atoms
1 mole of magnesium has a mass of 24g
12g of magnesium is equivalent to 1/2 moles = 0.5 moles of magnesium
12g of magnesium contains 1/2 moles of magnesium atoms = 0.5 x 6.02 x 1023 = 3.01 x 1023 magnesium atoms
The relationship between moles, mass and number of particles can be expressed by simple formulae:
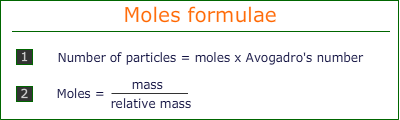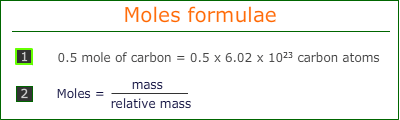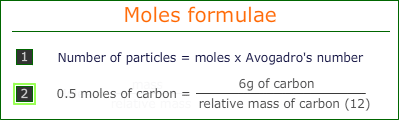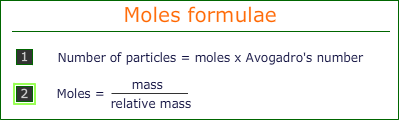
These formulae can be used to find any quantity when the other two quantities are known.
Note: The term "relative molecular mass" is no longer to be used.
Answer
|
Carbon has a relative mass of 12 and helium has a relative mass of 4 Carbon atoms are therefore 3 times bigger than helium atoms |
Q312-02 If 1 mole of magnesium atoms have a mass of 24g and 1 mole of helium atoms have a mass of 4g, how many times bigger is a magnesium atom than a helium atom?
Answer
|
1 mole is a term which means a very large number (Avogadro's number) of particles - in this case, atoms. So the same number of magnesium and helium atoms have masses of 24 g and 4 g respectively The mass ratio (relative masses) of the atoms magnesium and helium is 24 to 4 The mass ratio is 6:1 i.e. magnesium atoms are 6 times bigger than helium atoms |
Q312-03 Sulfur atoms have a relative mass of 32. What is the mass of one sulfur atom in grams?
Answer
|
1 mole of sulfur atoms have a mass of 32g. 1 mole of sulfur atoms contain 6.02 x 1023 sulfur atoms Therefore 1 sulfur atom has a mass = 32/6.02 x 1023 grams Therefore 1 sulfur atom has a mass = 5.32 x 10-23g |
Q312-04 Iron atoms have a relative mass of 56. What is the mass in grams of one iron atom?
Answer
|
1 mole of iron atoms have a mass of 56g. 1 mole of iron atoms equals 6.02 x 1023 iron atoms Therefore 1 iron atom has a mass = 56/6.02 x 1023 grams Therefore 1 iron atom has a mass = 9.30 x 10-23g |
Q312-05 If 1 sodium atom has a mass = 3.8 x 10-23g, calculate the mass of 1 mole of sodium atoms.
Answer
|
1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 atoms If 1 atom has a mass = 3.8 x 10-23 g Then 6.02 x 1023 atoms have a mass = 6.02 x 1023 x 3.8 x 10-23g 1 mole of sodium atoms have a mass = 22.9 g |
Q312-06 If 1 potassium atom has a mass = 6.48 x 10-23g, calculate the mass of 1 mole of potassium atoms.
Answer
|
1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 atoms If 1 atom has a mass = 6.48 x 10-23g Then 6.02 x 1023 atoms have a mass = 6.02 x 1023 x 6.48 x 10-23g 1 mole of potassium atoms have a mass = 39.0g |
Q312-07 How many atoms are present in 0.1 moles of iron?
Answer
|
1 mole of iron contains 6.02 x 1023 atoms of iron Therefore 0.1 moles contains 0.1 x 6.02 x 1023 atoms = 6.02 x 1022 atoms |
Q312-08 Calculate the number of atoms in 0.025 moles of silver.
Answer
|
1 mole of silver contains 6.02 x 1023 atoms of silver Therefore 0.025 moles contains 0.025 x 6.02 x 1023 atoms = 3.51 x 1022 atoms |
Q312-09 Calculate the mass of 3.01 x 1022 carbon atoms.
Answer
|
Carbon has a relative mass of 12 therefore 1 mole of carbon has a mass = 12g Therefore 6.02 x 1023 atoms of carbon = 12g Therefore 3.01 x 1022 carbon atoms has a mass = 12 x 3.01 x 1022/(6.02 x 1023)g Therefore 3.01 x 1022 carbon atoms have a mass = 0.6g |
Q312-10 Calculate the mass of 7.525 x 1022 lead atoms
Answer
|
Lead has a relative mass of 208 therefore 1 mole of lead has a mass = 208g Therefore 6.02 x 1023 atoms of lead = 208g Therefore 7.525 x 1022 lead atoms have mass = 208 x 7.525 x 1022/(6.02 x 1023)g Therefore 7.525 x 1022 lead atoms have mass = 26g |
External video resources
Applying the mole concepts: Richard Thornley
