Standard level
The characteristics, or properties of bonds formed by sharing electron pairs is examined in this section.
Syllabus ref: S2.2.3Structure 2.2.3 - A coordination bond is a covalent bond in which both the electrons of the shared pair originate from the same atom.
- Identify coordination bonds in compounds.
- AHL - Include coverage of transition element complexes.
Guidance
Tools and links
- AHL Reactivity 3.4 - Why do Lewis acid–base reactions lead to the formation of coordination bonds?
Dative covalent (coordination) bonds
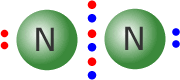
Usually, the two atoms involved in a covalent bond provide one electron each to make the pair. However, occasionally, both of the electrons come from one of the atoms. In this case, the bond is said to be dative (= giving) covalent. The fact that an electron pair is dative has no influence on the final structure.
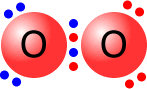
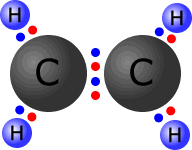
Ozone molecule
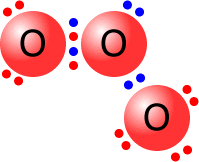
The central oxygen atom is bonded to one of the other oxygen atoms by a dative covalent bond (blue pair).
All of the oxygen atoms have a full outer shell (octet) of electrons.
Dative coordinate bonds are sometimes drawn as arrows in structural formulae.
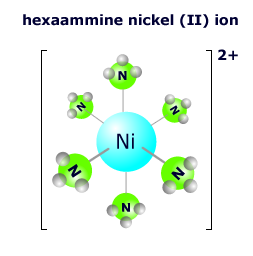
Ligand bonding in transition metal complex ions
The ligands that form bonds to the central transition metal ion coordinatea lone pair of electrons into suitably oriented orbitals from the transition metal 4th energy level.
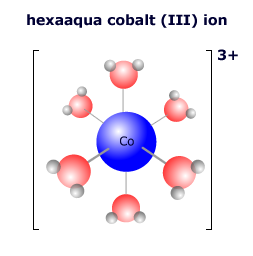
In the hexaaqua complex ion there is a lone pair coordinated from each oxygen atom of every water molecule to form the octahedral complex.
The hexaaquacobalt(III) complex ion
Multiple bonds including coordination bonds
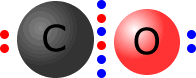
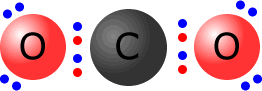
Dative coordinate bonds may also occur in conjunction with other covalent bonds. This is the case for carbon monoxide and its isoelectronic species, the cyanide ion.
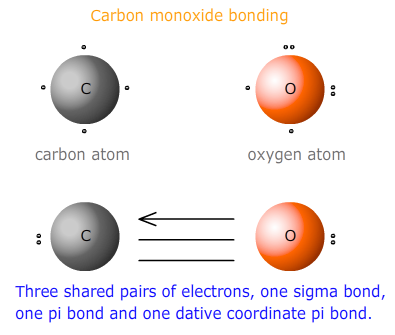
Worked examples
Q213-01 The most likely molecule to be formed by the reaction of boron and chlorine is:- BCl
- BCl3
- BCl4
- BCl6
|
Boron is in group 3 and has three valence electrons and a valency of 3. Each chlorine can share one pair to get a full outer shell. The final formula is BCl3 This is an electron deficient compound, as there are only six electrons in the outer shell of the boron atom. |
Q213-02 In which molecule would you find a triple covalent bond?
- O2
- N2
- O3
- FeCl3
|
Nitrogen is from group 5 of the periodic table. It needs to share three pairs of electrons to attain a full outer shell. Therefore the nitrogen molecule has three bonds per atom.
|
Q213-03 Which diatomic species should have the greatest bond dissociation energy?
- H2
- F2
- NO
- CO
|
The bond dissociation energy is the energy required to break the bond. It is a measure of the strength of the bond. The question is really asking "which has the strongest bond?". Triple bonds are stronger than double bonds which are stronger than single bonds. This time the triple bond is found in the carbon monoxide, CO molecule:
|
Q213-04 When C2H4, C2H2 and C2H6 are arranged in order of increasing C-C bond length what is the correct order?
- C2H6, C2H2, C2H4
- C2H4, C2H2, C2H6,
- C2H2, C2H4, C2H6
- C2H4, C2H6, C2H2
|
The stronger the bond the shorter it is, therefore the order we are looking for is triple. double, single bonds. This is the order of C2H2, C2H4, C2H6 |
Q213-05 Which statement is correct about two elements, whose atoms form a covalent bond with each other.
- The elements are metals
- The elements are non-metals
- The elements have very low electronegative values
- The elements have very different electronegativity values
|
Covalent bonds are normally formed between two non-metals (although not exclusively) |
Q213-06 Which of the following increases for the bonding between carbon atoms in the sequence of molecules C2H6, C2H4, C2H2?
- I - Number of bonds
- II - Length of bonds
- III - Strength of bonds
- I only
- I and III only
- III only
- I, II and III
|
The three molecules, ethane, ethene and ethyne have C-C bonds of single, double and triple in that order.
Therefore the correct answer is I and III only |
Q213-07 How do bond length and bond strength change as the number of bonds between two atoms increase?
| bond length | bond strength | |
| A | increases | increases |
| B | increases | decreases |
| C | decreases | decreases |
| D | decreases | increases |
|
Increasing bond number decreases bond length and increases bond strength = option D |
Q213-08 The length of the bond between carbon and oxygen is shortest in:
- CO
- CO2
- CH3CH2OH
- CH3CHO
|
In CO the two atoms are bonded by a triple bond. It is the shortest. |
Q213-09 Which molecule has the longest nitrogen - nitrogen bond length?
- N2
- N2F2
- N2H4
- N2H2
|
The longest bond length applies to a single bond. Only N2H4 contains an N-N single bond. |
Q213-10 In which of the following is there at least one double bond?
- I - O2
- II - CO2
- III - C2H4
- I only
- III only
- II and III only
- I,II and III
|
| ^ top |