Standard level
Prior to the discovery by Freidrich Wöhler in 1828 that urea could be made by evaporation of ammonium thiocyanate solution, it was thought that organic chemicals could only be produced by the hand of a God. Nowadays our definitions of organic chemistry are not quite so stringent...
Syllabus ref: S3.2.2Structure 3.2.2 - Functional groups give characteristic physical and chemical properties to a compound.
- Organic compounds are divided into classes according to the functional groups present in their molecules.
- Identify the following functional groups by name and structure: halogeno, hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, alkoxy, amino, amido, ester, phenyl.
Guidance
- The terms “saturated” and “unsaturated” should be included.
Tools and links
- AHL Structure 2.4 - What is the nature of the reaction that occurs when two amino acids form a dipeptide?
- Nature of science, Reactivity 3.2, Reactivity 3.4 - How can functional group reactivity be used to determine a reaction pathway between compounds, e.g. converting ethene into ethanoic acid?
Carbon compounds
Carbon atoms possesses some remarkable properties.
- They can form strong, stable covalent bonds to other carbon atoms and many different types of atom.
- They can build up chains of carbon atoms to form a carbon 'skeleton'. (catenation - literally 'chain making')
- They can form multiple bonds, both with other carbon atoms or chains, and with other elements.
These three factors allow carbon to produce, literally, millions of different compounds, many of which are found in living systems. The definition of organic compound is now taken to mean a compound of carbon that is not a simple mineral compound. Again, this is pretty vague, but means that carbonates, hydrogen carbonates and oxides are excluded from the definition.
Carbon is often bonded to hydrogen and oxygen in its compounds. Those compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen only are called hydrocarbons.
Functional groups
The average bond strength of a carbon - carbon single bond is 346 kJ mol-1 and a carbon = carbon double bond has a bond strength of 602 kJ mol-1.
To break carbon-carbon bonds requires large amounts of energy, meaning that the carbon skeleton is particularly stable. Organic compounds react in many different ways, but the carbon skeleton is rarely broken. For this reason, the atoms that are attached to the carbon skeleton are very important as they often confer reactivity to the molecule. Such atom or groups are called 'functional groups' - they give the molecule functionality.
Essentially, functional groups are considered to be any atom or groups of atoms that does not consist of carbon, hydrogen and single bonds only.
 |
 |
 |
|
Alkenyl
|
Alkynyl
|
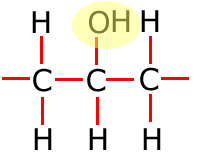
Hydroxyl
|
|
|
||
 |
 |
 |
|
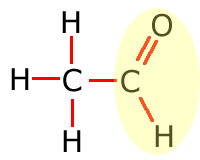
Aldehyde (carbonyl)
|
Ketone (carbonyl)
|
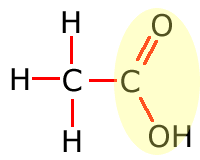
Carboxyl
|
Common functional groups
Groups or atoms may also be used to join two carbon chains together. Such groups are sometimes called 'linkages'
Linkage groups
| Linking atom or group | name |
| O | ether link |
| -COO- | ester link |
| -NHCO- | amide (or peptide) link |
| -O-O- | peroxo link |
Unsaturated compounds
Carbon is able to undergo catenation (chain formation) giving rise to an infinite number of structures. It is also able to bond to itself using more than one pair of electrons, creating double or even triple bonds.
Molecules that have double bonds are said to be "unsaturated" as they have the potential to add more hydrogen atoms into the stucture.
The term 'saturation' and unsaturation' refer to the types of bonds that make up the carbon skeleton. Double and triple bonds are said to be 'unsaturated', whereas a molecule that contains only single carbon-carbon bonds is said to be 'saturated'.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbon chains containing a double bond are said to contain an alkenyl group.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbon chains containing a triple bond are said to contain an alkynyl group.
Worked examples
Q1011-01 Which element is present in all organic compounds?- carbon
- nitrogen
- oxygen
- phosphorous
|
Carbon as it is by definition the element of organic compounds. |
Q1011-02 Which statement explains why the element carbon forms so many compounds?
- Carbon atoms combine readily with oxygen.
- Carbon atoms have very high electronegativity.
- Carbon readily forms ionic bonds with other carbon atoms.
- Carbon readily forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms.
|
Carbon readily forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms - catentation. |
Q1011-03 In a molecule of CH4, the hydrogen atoms are spatially oriented toward the centers of a regular:
- pyramid
- tetrahedron
- square
- rectangle
|
When carbon uses four pairs of electrons to form four covalent bonds to four different atoms it has the bonds separated as far apart as possible in space. This is a tetrahedral arrangement in which the bond angle is 109º 28'. |
Q1011-04 What is the maximum number of covalent bonds than an atom of carbon can form?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
|
Carbon forms a maximum of four single covalent bonds. |
Q1011-05 What is the total number of sigma bonds found in the following compound?
CH3-CH=C=CH-C |
- 8
- 10
- 11
- 15
|
Sigma bonds must always be formed BEFORE a double or triple bond. Thus all of the bonds joining atoms together are made up of one sigma bond. There are 11 links between atoms therefore there are 11 sigma bonds |
Q1011-06 What is the total number of pi bonds found in the following compound?
HC |
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
|
The triple bond consists of one sigma and two pi bonds, therefore there are two pi bonds in the molecule. |
Q1011-07 Which of the following molecules has the shortest carbon to carbon bond distance?
- H3C-CH3
- H2C=CH2
- HCCH
- H2C=C=O
|
Triple bonds are shorter and stronger than double or single therefore the answer is: HC |
Q1011-08 Which of the following statements best describes a functional group?
- It is an atom or group of atoms which gives a compound its characteristic propertles.
- It is a highly reactive group of atoms with noble gas configurations.
- It is a highly reactive group of atoms which lack noble gas configurations.
- It is the non-polar part of an organic molecule.
|
A functional group is any atom group of atoms which is not a saturated hydrocarbon structure. The functional group confers characteristic properties on a compound. Response A. |
Q1011-09 Which of the following is the best description of a 'linkage'?
- It is an atom or group of atoms at the end of a carbon chain.
- It is a highly reactive group of atoms with noble gas configurations.
- It is an atom or group of atoms that joins two hydrocarbon chains together.
- It is an atom or group of atoms that, together with another atom or group
of atoms, makes up a functional group.
|
It is a group of atoms or one atom that joins two hydrocarbon chains together, such as an oxygen atom in the case of ethers, or a -COO- group in the case of esters. |
Q1011-10 Enthalpies of reaction for example, combustion, can be calculated using average bond enthalpies or enthalpies of formation. The two methods give closer results for cyclohexane than they do for benzene. Explain this difference.
Answer
|
Benzene has a delocalised ring of electrons around the molecule, making the bonds intermediate in character between double and single bonds. This structure is relatively more stable than a simple structure with alternating double and singe bonds, and this is reflected in the enthalpy changes of its reactions. |
 C-H
C-H