Standard level
Active metals react stoichiometrically with water or dilute acid making hydrogen gas.

Background
A sample of a reactive metal, for example lithium or calcium with react steadily, but safely with water making hydrogen gas. The gas can be collected and its volume measured over water. If the ambient pressure and temperature are known, then the moles of gas and hence its relative mass may be determined.
Reaction of lithium with water
2Li(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2LiOH(aq) + H2(g)
Reaction of calcium with water
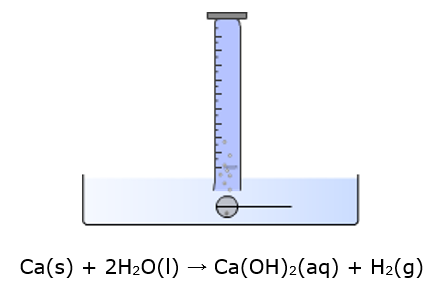
Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
Note: "Phyphox" is a free app available on many smart phones. It is a rapid and easy way to obtain the ambient pressure.
The ambient temperature can be measured using laboratory thermometers or temperature probes.
Chemicals
- Lithium
- Calcium
- Tap water
Apparatus
- Large measuring cylinder, 250ml or 500ml
- Tea diffuser
- Water trough or plastic tray
- Electronic balance
- Metal scalpel
- White tile
- Thermometer
- Phyphox app
- • Weigh one small piece of clean calcium on the digital balance (use a watch glass).
- • Place the calcium into a dry tea diffuser using tweezers.
- • Fill a plastic tray with water (the depth needs to be greater than the width of the diffuser).
- • Place a 250ml measuring cylinder upside down and full of water into the tray. There must be enough water depth to allow the tea diffuser to pass under the measuring cylinder without loss of water from the measuring cylinder.
- • Quickly raise the measuring cylinder slightly (but not above the water level!) and place the tea diffuser below the mouth of the cylinder.
- • Record the initial level of the water and the final level after gas evolution has ceased.
- • Remove, rinse and dry the tea diffuser and repeat the experiment.
Do not attempt this experiment with sodium or potassium. They are too reactive for safe handling with water.
The hydrogen gas collected is highly flammable and should be vented safely in a fume cupboard.
The solution produced in the trough (or tray) is caustic and could cause burns to skin. In case of contact rinse with tap water.