Standard level
Increasing the temperature increases the average kinetic energy of the reacting particles.

Background
Controlling the temperature of a reaction mixture usually involves the use of a water bath to create a controllable environment.
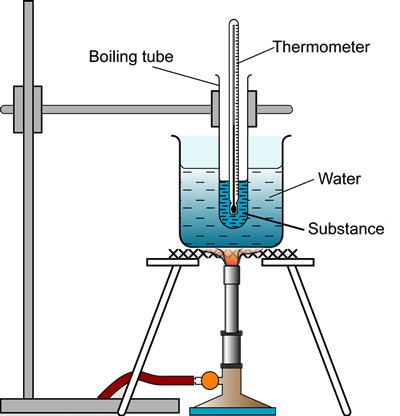
To investigate the concepts that can affect reaction rate it is important to choose reactions that have a reactant or product that can be monitored in such a way as its concentration can be determined.
Reactions that produce a gas allow the products to be monitored and measured. In this case, the oxidation reaction of hydrogen peroxide with potassium iodide in acidic solution produces iodine that is detected using starch indicator. However, if a small, known amount of sodium thiosulfate is added this reacts with the iodine produced and removes it from the reaction before it can react with the starch. When the sodium thiosulfate is used up the starch - iodine complex colour suddenly appears. This is called an iodine clock reaction.
Reaction of hydrogen peroxide with iodide ions
H2O2(aq) + 2I-(aq) + 2H+(aq)→ 2H2O(l) + I2(aq)
Reaction of iodine with thiosulfate ions
I2(aq) + 2S2O32-(aq)→ 2I-(aq) + S4O62-
Chemicals
- Sodium thiosulfate(aq), 0.02 mol dm-3
- Potassium iodide(aq), 0.2 mol dm-3
- Starch(aq)
- Hydrogen peroxide(aq), 0.997 mol dm-3
- Ethanoic acid(aq), 0.5 mol dm-3
Apparatus
- Tripod, gauze, small Bunsen burner
- Stopwatch
- Burette, 50ml (x4)
- Water bath
- Test-tubes and rack
- Fill one test tube with potassium iodide (8cm3), sodium thiosulfate (8cm3) and starch solution (8cm3).
- Fill the second test tube with ethanoic acid (8cm3) and hydrogen peroxide (8cm3).
- Mix the two test-tube contents in a small (50cm3) conical flask and start the timer. Record the time taken for the appearance of the starch iodide complex colour.
- Measure the temperature of the mixture.
- Repeat for reliability twice more.
- Repeat the experiment after first allowing the test-tubes to stand in hot water for 2 minutes.
- Repeat the experiment after allowing the test-tubes to stand in hot water for 4 minutes, 6 minutes and 8 minutes.
- Record all data.
- An ice/salt/water bath is also available to reduce the temperature of the two test-tubes before mixing.
Quantities to use:
- Sodium thiosulfate 8 cm3
- Potassium iodide: 8 cm3
- Ethanoic acid: 8 cm3
- Hydrogen peroxide: 8 cm3
- Water/starch 8 cm3
- Hydrogen peroxide is an oxidising agent.