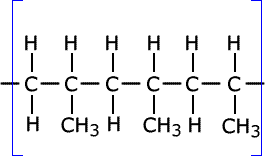
Higher-level only
The mechanisms of electrophilic addition proceeds via a carbocation (carbonium ion). In the asymmetric electrophilic reaction the stability of this carbocation determines the mechanistic route taken and the major product.
Syllabus ref: R3.4.12Reactivity 3.4.12 - The relative stability of carbocations in the addition reactions between hydrogen halides and unsymmetrical alkenes can be used to explain the reaction mechanism. (HL)
- Predict and explain the major product of a reaction between an unsymmetrical alkene and a hydrogen halide or water.
Guidance
Tools and links
Addition to asymmetric alkenes
Asymmetric alkenes have different groups on either side of the double bond. For example propene, CH2CHCH3.

When electrophilic addition occurs with an asymmetric alkene there is a choice of possible products.
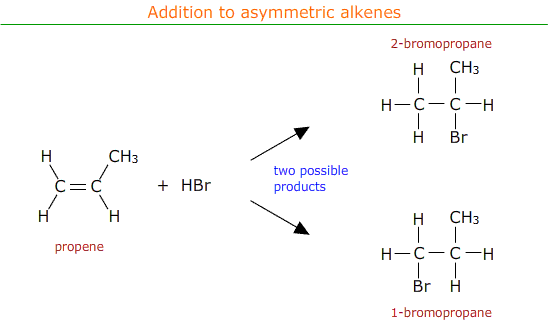
In practise both of the possible products are formed, but in different amounts. There is a major product with a higher percentage yield and a minor product with a lower percentage yield.
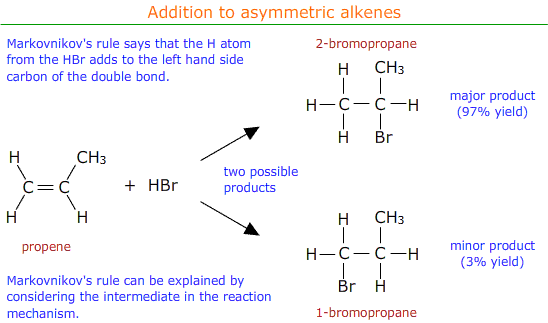
Markovnikov's rule can be applied to predict the major product.
Markovnikov's rule
Markovnikov's rule says that the hydrogen atom from the electrophile (HBr in this case) preferentially adds to the carbon atom of the double bond that already has the most hydrogen atoms attached.
It may be seen that in the above example the major product is 2-bromopropane.
The major and minor products can be explained in terms of the relative stability of the two possible carbo-cation intermediates formed in the reaction mechanism.

Asymmetric electrophilic addition
Worked examples
Q1032-01 The presence of a carbon-carbon double bond in an organic molecule:- results in a linkage between carbon atoms that has a much smaller bond energy that that of single carbon to carbon bonds.
- results in greater reactivity, often with addition of two atoms to the two carbon atoms of the bond.
- makes the molecule much more polar and therefore much more soluble in water.
- allows internal molecular rotations so that there are no isomers with the same formula possible.
|
The double bond overall is stronger than a single carbon bond, but little energy is required to break the pi system and open the double bond. Hence a double bond results in greater reactivity, often with addition of two atoms to the two carbon atoms of the bond. Response B |
Q1032-02 Which product is formed by the reaction between CH2CH2 and HBr
- CH3CH2Br
- CH2CHBr
- BrCHCHBr
- CH3CH2Br2
|
This is a hydrohalogenation addition reaction producing CH3CH2Br |
Q1032-03 What type of reaction does the equation below represent?
CH2=CH2 + Br2 → BrCH2CH2Br
- Substitution
- Condensation
- Reduction
- Addition
|
This is an addition reaction, or more specifically, electrophilic addition. |
Q1032-04 Which of the following statements about single and double bonds between two carbon atoms is (are) correct?
- I. double bonds are stronger than single bonds
- II. double bonds are more reactive than single bonds
- I only
- II only
- Both I and II
- Neither I nor II
|
Both of the statements are correct, response C |
Q1032-05 Name the type of polymerisation reaction that C3H6 undergoes and draw the structure of a section of the polymer chain formed from three monomer molecules.
Answer
|
C3H6 is propene and polymerises by addition polymerisation.
|
Q1032-06 A gaseous alkane and a gaseous alkene are treated separately in the following ways. Which treatment will distinguish between them?
- They are ignited in excess oxygen
- They are passed over heated copper
- They are bubbled through an aqueous solution of bromine
- They are bubbled through an aqueous solution of propanal
|
Bubbling both gases through aqueous bromine can distinguish them. In the case of the alkene the orange bromine solution becomes decolourised. There is no change in the case of the alkane. |
Q1032-07 Polymers formed from monomers with the general formula H2C=CHX
- Have the same percentage of carbon as the monomer
- Are produced by substitution reactions
- Contain C=C bonds
- Are more reactive than the monomer
|
As the empirical formula of the alkene and the polymer is the same they both have the same percentage composition. |
Q1032-08 Which compound is most likely to be a starting material for a common polymer?
- CH3CH2CH3
- CH3CH2OH
- CH3CHCH2
- C6H5CH3
|
Addition polymers are made from alkenes. The only alkene among the choices is CH3CHCH2 |
Q1032-09 In the reaction below state the type of reaction and identify the reagent and conditions needed.
C2H4 → CH3CH2OH
Answer|
This is an addition reaction. The reagent is water in the form of steam. The gases must be passed over a phosphoric acid catalyst at 300ºC. |
Q1032-10 C2H4 can be converted into one of the compounds below in a single step reaction
- C2H3Cl
- C2H4Cl2
Identify the compound that can be formed directly from C2H4
|
Addition of chlorine to ethene produces the compound C2H4Cl2 by addition. |