Standard level
There are four fundamental forces in nature that can act over a distance. We are very familiar with gravity, for example, and accept that it acts on any object in a gravitational field.
Two of the other forces are applicable only to the nuclei of atoms and, as such, do not concern us here. The fourth force is the electromagnetic force.
This has various manifestations, such as a magnetic field acting on magnetic materials. One other manifestation of this force is the electrostatic field that is associated with charged particles. This is the force responsible for the structure of all matter.
Syllabus ref: S1.1.1Structure 1.1.1 - Elements are the primary constituents of matter, which cannot be chemically broken down into simpler substances.
- Compounds consist of atoms of different elements chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio.
- Mixtures contain more than one element or compound in no fixed ratio, which are not chemically bonded and so can be separated by physical methods.
- Distinguish between the properties of elements, compounds and mixtures.
Guidance
Tools and links
- Tool 1 - What factors are considered in choosing a method to separate the components of a mixture?
- Tool 1 - How can the products of a reaction be purified?
- Structure 2.2 - How do intermolecular forces influence the type of mixture that forms between two substances?
- Structure 2.3 - Why are alloys generally considered to be mixtures, even though they often contain metallic bonding?
Atoms and molecules, elements and compounds
The most basic building blocks of matter are small particles called atoms. These majority of these atoms are fundamentally unstable in the natural world and achieve stability by joining together with other atoms, either of the same kind, or of different kinds. When small numbers of atoms join together (bond) the particles formed are known as molecules.
When large numbers of the same type of element conglomerate together, the substance formed is called an element. There are about 90 different kinds of atom, therefore there are about 90 different kinds of naturally occurring elements.
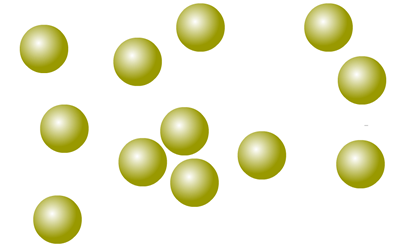
Elemental xenon is made up of individual atoms
Elemental iodine is made up of pairs of iodine atoms in individual molecules
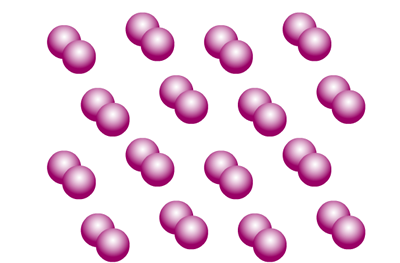
There are about 90 different types of atom that occur naturally. Their differences are explored in the section on atomic theory.
If the smallest particles themselves are made up of two or more different atoms, then the substance is said to be a compound.
Compounds
Compounds are substances that contain two or more elements chemically combined. Their smallest particles may be discrete molecules, giant molecules or charged particles called ions.
The law of constant composition
This says that the ratio of elements within a compound is always the same regardless of the source of the compound. Put in simple terms, it means that the compound can only ever be one substance and it can be represented by a chemical formula that shows the ratio of atoms of each type of element within the compound.
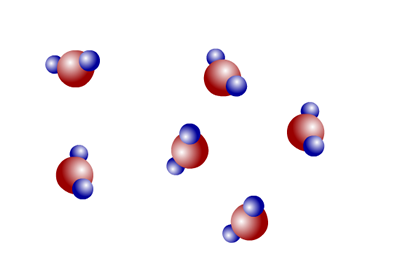
Water is a compound of hydrogen and oxygen. The smallest particles of water are molecules and every molecule has two hydrogen atoms chemically bonded to one oxygen atom. It can be represented by a chemical formula, H2O.
Water is a compound made up of molecules with two different atoms
Pure substances and mixtures
When all of the particles in a substance are the same, we say that the substance is pure, as it cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical means.
If there is more than one type of particle in the substance then it is considered to be a mixture. Alloys are mixtures as there is no fixed ratio between their components.
Brass is a mixture of zinc and copper atoms.
There is one important exception to the statements above, and that is the case of an ionic compound. Ionic compounds contain an exact ratio of two or more types of charged particles (ions). Ionic compounds have a fixed chemical composition and hence formula.
The properties of elements, compounds and mixtures
Probably the most important difference between elements, compounds and mixtures is that elements and compounds cannot physically be separated into simpler substances.
Clearly, elements contain only one type of atom making it impossible to get anything simpler. Compounds however, contain more than one type of element, but these are chemically bonded to one another in the form of molecules or ions. The only way that they can be separated is to break these bonds and that requires chemical reaction.
Water is made up of molecules that each contain two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom chemically bonded together. To break these bonds we can use electrolysis, i.e. we subject the water to a electrical potential that causes the bonds to break and we can get oxygen and hydrogen separately. The way this happens is actually a little more complex, but the end result is the same, one compound is broken to produce two elements.
2H2O → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
Elements and compounds are pure substances, they exhibit fixed physical and chemical properties.
Mixtures have properties that depend on the proportions of each component in the mixture.
Separation of mixtures
Mixtures can be separated by physical means. As the mixture contains two or more substances simply mixed together and not bonded, then we can apply different techniques to separate them. These are tools available to the chemist for separation.
- Filtration
- Distillation
- Decantanting
- Chromatography
This is not an exhaustive list, and the techniques chosen will depend on the nature of the substances in the mixture. Mixtures can take a wide variety of forms as all three states of matter can be involved. Usually, there is a major component and a minor component in the mixture.
Examples of mixtures in everyday life
- A solution is a mixture of a solute in a solvent (usually water)
- Smoke is a mixture of a solid in a gas
- Milk is a mixture of fat particles (and other substances) dispersed in water
- Wine is a mixture of two miscible liquids, water and ethanol (and many other minor components)
Mixtures may appear to be all in the same phase (physically distinct state) in which case they are said to be homogeneous, or there may be obvious phase bondaries (we can see the join) in which case they are said to be heterogeneous.
Wine is a homogeneous mixture, salt and sand is a heterogeneous mixture.
In summary
- The atoms of group 18 elements can exist on their own.
- Two or more atoms chemically combined is called a molecule
- A substance that consists of only one type of atom is called an element.
- A substance that consists of particles containing more than one type of atom is called an compound.
- Ionic substances are an exception in which the particles carry electrical charges.
External video resources
Elements, compounds and mixtures: Richard Thornley