Standard level
Covalent bonds may be single, double or triple. This section looks at the effect of bond length on bond energy, as well as the impact of multiple bonds.
Syllabus ref: S2.2.2Structure 2.2.2 - Single, double and triple bonds involve one, two and three shared pairs of electrons respectively.
- Explain the relationship between the number of bonds, bond length and bond strength.
Guidance
Tools and links
- Reactivity 2.2 - How does the presence of double and triple bonds in molecules influence their reactivity?
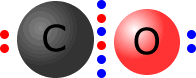
Double and triple bonds
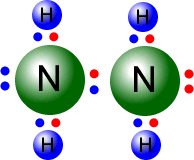
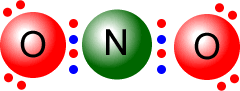
A double bond is shown as two shared pairs of electrons, each of the bonded
atoms provide two electrons for the bond. In the oxygen molecule at the left,
their are two shared pairs of electrons giving a stable octet (eight) of electrons
around each oxygen atom. 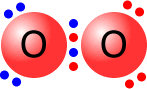
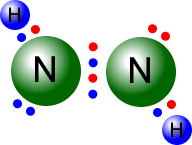
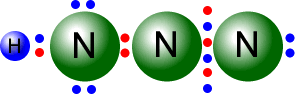
In triple bonds there are three pairs of electrons holding the two atoms
together. The molecule shown at the right is the ethyne (acetylene) molecule.
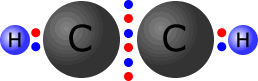 Each
of the carbon atoms (group IV) originally started with 4 outer electrons.
In the ethyne molecule at the right, both of the carbon atoms now have a full
octet (eight) of electrons and the two hydrogen atoms have a full first shell,
with two electrons. There are no non-bonding pairs.
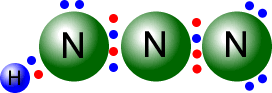
Each
of the carbon atoms (group IV) originally started with 4 outer electrons.
In the ethyne molecule at the right, both of the carbon atoms now have a full
octet (eight) of electrons and the two hydrogen atoms have a full first shell,
with two electrons. There are no non-bonding pairs.
Length and strength of covalent bonds
A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons in which the electron charge density lies along the inter-nuclear axis. This attracts the nucleus of each bonded atom holding them together.
The bond is a result of the two electrostatic forces, nucleus-electrons and electrons-nucleus.
The greater the electron density between the two nuclear centres, the greater the electrostatic force and the stronger the bond.
Hence, double bonds are shorter and stronger than single bonds.
The size of the atoms is also a factor in bond strength, as smaller atoms have the bonding electrons closer to the nuclei where they can exert a stronger electrostatic force. In general, short bonds are stronger bonds.
| Bonding pairs | Lone pairs | |
| A. | 8 | 4 |
| B. | 7 | 5 |
| C. | 7 | 4 |
| D. | 5 | 5 |
|
The best way is to draw out the structure:
Counting up there are 4 lone pairs and 8 bonding pairs. |
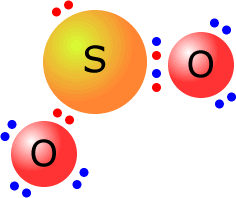
Q215-02 What is the Lewis (electron dot) structure of sulfur dioxide?
Answer
|
Sulfur dioxide has the formula SO2. Sulfur has six valence (outer shell) electrons and each oxygen also has six valence (outer shell) electrons, giving a total of 18. By double bonding one of the oxygens to the sulfur, the oxygen and sulfur now have a full octets. The sulfur can then donate a pair of electrons into the second oxygen's outer shell to leave all the atoms with full octets
|
Q215-03 Butane, C4H10, propanal, C3H6O and propan-1-ol, C3H8O have very similar molar masses (59±1). Draw the Lewis structures of each of these molecules.
Answer
|
||||||
Q215-04 Hydrazoic acid can be represented by two possible Lewis structures, in which the atoms can be arranged as NNNH. Draw the two possible Lewis structures of N3H
Answer
|
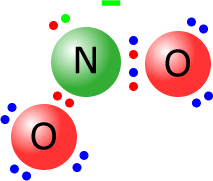
Q215-05 Draw Lewis structures of each of the following species, NO2- and NO2+
Answer
|
With the negative ion, NO2-, you have to add one electron to the structure. So N (5 valence electrons ) and 2 x oxygen (six valence electrons) = 17 electrons + 1 for the negative charge = 18 electrons. With the positive ion, NO2+, you have to subtract one electron from the structure. So N (5 valence electrons ) and 2 x oxygen (six valence electrons) = 17 electrons - 1 for the negative charge = 16 electrons.
|
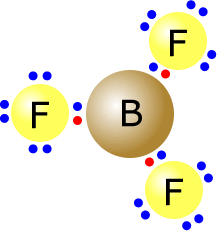
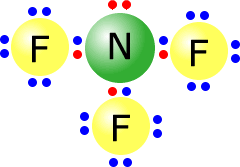
Q215-06 Draw Lewis structures to represent BF3 and NF3
Answer
|
Q215-07 Write two Lewis electron dot structures for the methanoate ion HCOO-
Answer
|
Q215-08 Write Lewis electron dot structures for H2NNH2 and HNNH. What bond angle is expected for the H-N-N atoms is each molecule?
Answer
|
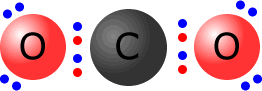
Q215-09 Draw Lewis (electron dot) structures for CO2 showing all valence electrons.
Answer
|
Count up the available valence electrons:
Connect both of the oxygen atoms to the central carbon by a double bond. O=C=O This uses up four pairs of electrons, leaving four pairs to place on the structure, so that all atoms have a full octet.
|
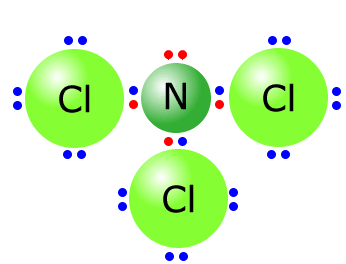
Q215-10 Draw the Lewis structure of NCl3. Predict giving a reason the Cl-N-Cl bond angle in NCl3
Answer
|
| ^ top |
.gif)