Standard level
'Iso' derives from the Greek word 'isos', meaning 'equal'. 'Mer' derives from the Greek word 'meros', meaning 'parts'. Isomers = having equal parts.
Isomers contain exactly the same atoms in number and quantity, but with a different arrangement.
Syllabus ref: S3.2.6Structure 3.2.6 - Structural isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula, but different connectivities.
- Recognize isomers, including branched, straight-chain, position and functional group isomers.
Guidance
Tools and links
- Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols, halogenoalkanes and amines should be included.
- AHL Structure 2.2 - How does the fact that there are only 3 isomers of dibromobenzene support the current model of benzene’s structure?
Structural isomerism
Isomerism means molecules that have the same molecular formula, but differ in the arrangement of their atoms relative to one another, either structurally or spatially.
Structural isomers have the same molecular formula, but differ in their arrangement of atoms. They may have a different arrangement of the same structural groups or they may have a different arrangement of atoms, giving rise to different functional groups.
Positional isomerism
This may be caused by branching, or positioning the functional groups on different carbon atoms in the main carbon chain.
|
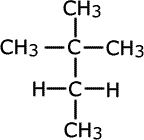
methylbutane
|
dimethylpropane
|
 |
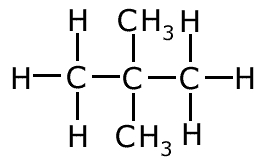 |
The two molecules above both have the molecular formula C5H12, but have a different arrangement of carbon atoms. In the first case the longest chain is four carbon atoms long and in the second case it is three carbon atoms long. The two molecules are identical in molecular formula and belong to the same homologous series, but have different structures.
|
butan-1-ol
|
butan-2-ol
|
 |
 |
In the two molecules above, the only difference is the position of the functional group. This is an example of positional isomerism.
Functional group isomerism
Functional group isomers have their atoms arranged differently in the isomers giving rise to different functional groups.
|
ethenol
|
ethanal
|
 |
 |
In this example the molecule ethenol has two functional groups, a double bond and an alcohol group. In the ethanal molecule there is only one functional group, the aldehyde (alkanal) group. Changing the arrangement of the atoms has changed the nature of the functional groups.
Worked examples
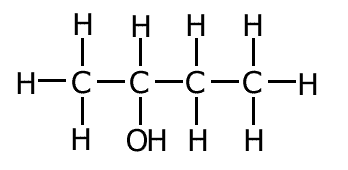
Q1016-01 How many structural isomers can be obtained by replacing a hydrogen atom of the following compound by a chlorine atom?
|
The correct answer is 5.
|
Q1016-02 Consider the hydrocarbons identified by the numbers 1 through 5 below:
- CH3CH2CH2CH3
- CH3CH=CHCH3
- CH3CH2CH3
- (CH2)4
- CH3C
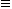 CCH3
CCH3
Which pair of the above compounds are isomers?
- 1 and 4
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 2 and 5
|
Compounds 2 and 4 both have the same molecular formula and are therefore isomers |
Q1016-03 Which compounds are isomers?
- 1-propanol and 2-propanol
- methanoic acid and ethanoic acid
- methanol and methanal
- ethane and ethanol
|
Both 1-propanol and 2-propanol are isomers |
Q1016-04 How are the following compounds related?
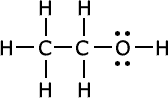 |
 |
- isobars
- isotopes
- isomers
- these compounds are not related at all...they are totally different.
|
Yup, they are isomers, they have the same molecular formula, C2H6O |
Q1016-05 What is the correct IUPAC name for the hydrocarbon shown below?
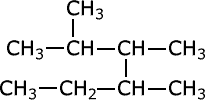
- Nonane
- 2-ethyl 3,4-dimethylpentane
- 3,4,5-trimethylhexane
- 2,3,4-trimethylhexane
|
It is correctly called 2,3,4-trimethylhexane |
Q1016-06 A straight-chain alkane contains eight carbon atoms. Its molecular formula is
- C8H8
- C8H14
- C8H16
- C8H18
|
The general formula of alkanes is CnH2n+2, therefore octane has the molecular formula C8H18 |
Q1016-07 How many different structural isomers can be made with the formula C4H9Cl ?
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
|
There are four isomers possible:
|
Q1016-08 Which names are correct for the following isomers of C6H14?
 |
|
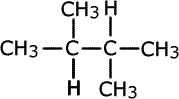 |
| 2-methylpentane | 2-ethylmethylpropane | 2,3-dimethylbutane |
- I only
- II only
- II and III only
- I and III only
|
Structures I and III are correctly named. |
Q1016-09 How many structural isomers are possible with the molecular formula C6H14
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
|
There are 5 possible: hexane, 2-methylpentane, 3-methylpentane, 2,2-dimethylbutane, 2,3-dimethylbutane. |
Q1016-10 Which formulas represent butane or its isomers?
- I. CH3(CH2)2CH3
- II. CH3CH(CH3)CH3
- III. (CH3)3CH
- I only
- I and II only
- I and III only
- II and III only
|
Correct response II and III only |